-
자바 데이터 타입, 변수 그리고 배열자바 스터디 2020. 12. 31. 18:43
백기선님의 Java 스터디를 진행하며 찾아본 내용입니다.
목표
자바의 프리미티브 타입, 변수 그리고 배열을 사용하는 방법을 익힙니다
학습할 것
- 프리미티브 타입 종류와 값의 범위 그리고 기본 값
- 프리미티브 타입과 레퍼런스 타입
- 리터럴
- 변수 선언 및 초기화하는 방법
- 변수의 스코프와 라이프타임
- 타입 변환, 캐스팅 그리고 타입 프로모션
- 1차 및 2차 배열 선언하기
- 타입 추론, var
1. 프리미티브 타입 종류와 값의 범위 그리고 기본 값
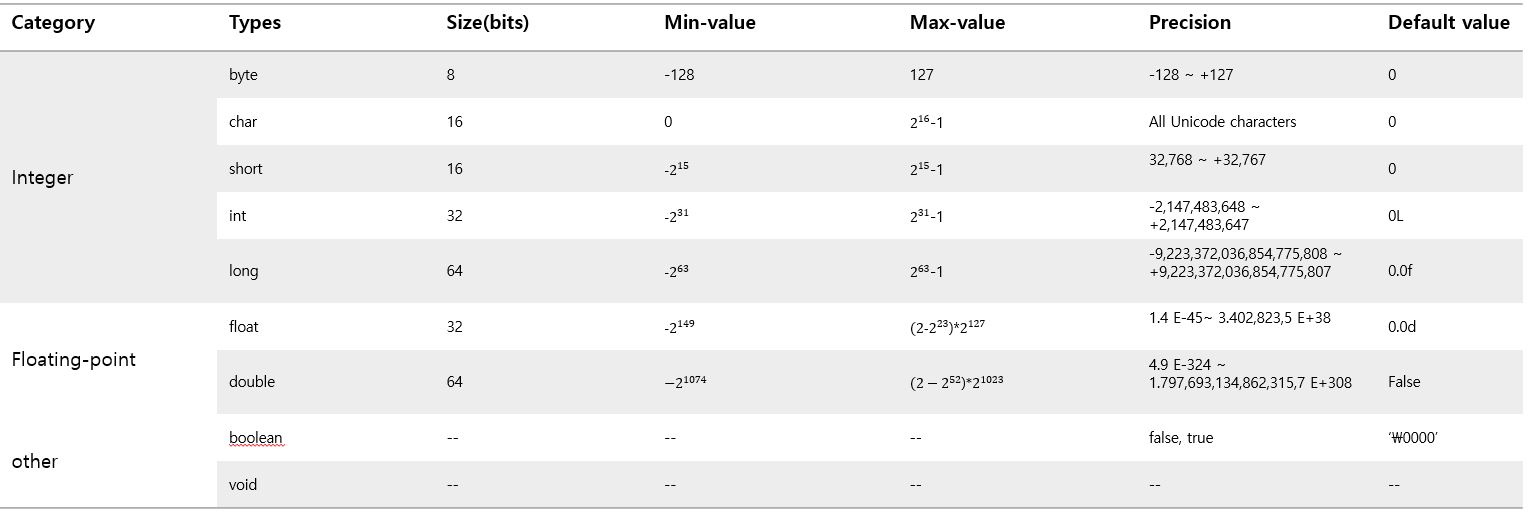
프리미티브 타입 종류와 값의 범위 2. 프리미티브 타입과 레퍼런스 타입
레퍼런스 타입은 다음과 같은 것들을 포함한다
- Annotation
- Array
- Class
- Enumeration
- Interface
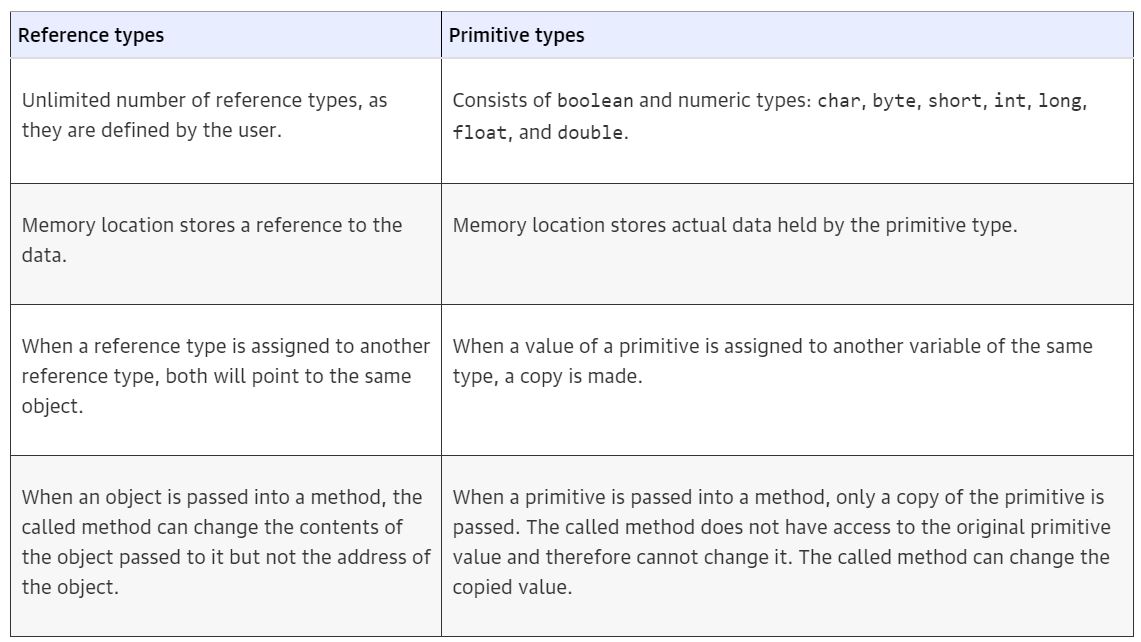
Reference types vs Primitive type - https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/java-8-pocket/9781491901083/ch04.html 3. 리터럴
변수에 할당 할 수 있는 모든 상수 값을 리터럴(Literal)/상수(Constant)라고 한다.
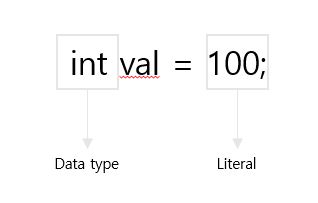
Literal Literal은 다음과 같이 나눌 수 있다
1) Integer Literal
Decimal Literal (Base 10)
int x = 101;Octal literals (Base 8)
// The octal number should be prefix with 0. int x = 0146;Hexa-decmal(Base 16)
// The hexa-decimal number should be prefix // with 0X or 0x int x = 0X123Face;Binary Literals(0 or 1)
int x = 0b1111;2) Floating-Point Literals
float 타입은 F로 끝나거나 f로 끝냄
그 외의 나머지 타입은 double
3) Character and String Literal
- Unicode character
- special escape character
- \b(backspace)
- \t(tab)
- \n(line feed)
- \f(form feed)
- \r(carriage return)
- \"(double quote)
- \'(single quote)
- \\(back slash)
4.변수 선언 및 초기화하는 방법
class A { // primitive type variable declaration & initialization int variable = 1; } class B { public static void main(String[] args) { // reference type variable declaration & initialization A a = new A(); System.out.println(a.variable); } }5. 변수의 스코프와 라이프타임
자바에서 변수는 오직 생성된 영역내에서만 액세스 할 수 있는데 이를 "scope"라고 한다
Instance Variables
- 클래스 안에서 선언되었지만 메소드 및 블록 외부에서 선언 된 변수
- Scope: static 메소드를 제외한 클래스 전체
- Lifetime: object가 메모리에 남아있을 때까지
Class Variables
- 클래스 내부, 모든 블록 외부에서 선언되고 static으로 표시된 변수
- Scope: 전체 클래스
- Lifetime: 프로그램이 끝날때까지 또는 클래스가 메모리에 로드되는 도중
Local Variable
- 인스턴스 및 클래스 변수가 아닌 다른 모든 변수
- Scope: 선언된 블록 내부
- Lifetime: 선언된 블록을 내부에 있는 도중
6. 타입 변환, 캐스팅 그리고 타입 프로모션
하나의 primitive 데이터 유형을 다른 데이터 유형으로 변환하는 것.
Widening 혹은 Narrowing 두 가지 방법으로 캐스팅 할 수 있음Widening
- 작은 데이터 타입을 큰 데이터 타입으로 변환하는 것

Widening - https://www.tutorialspoint.com/what-is-type-conversion-in-java#:~:text=Type%20Casting%2Ftype%20conversion,datatype%20is%20known%20as%20widening. Narrowing
- 큰 데이터 타입을 작은 데이터 타입으로 변환하는 것
- 컨버팅 하기 위해선 명시적으로 "( )"를 사용해야 함

Narrowing - https://www.tutorialspoint.com/what-is-type-conversion-in-java#:~:text=Type%20Casting%2Ftype%20conversion,datatype%20is%20known%20as%20widening. import java.util.Scanner; public class NarrowingExample(String args[]) { public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter an integer value: ") int i = sc.nextInt(); char ch = (char) i; System.out.println("Character value of the given integer: " + ch); } }7. 1차 및 2차 배열 선언하기
class A { public static void main(String args[]) { // declare 1 dimensional array int[] array1dim = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} // declare 2 dimensional array int[] array2dim = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}} } }8. 타입 추론, var
- 'var' 키워드는 자바 10(JDK 10)에서 추가된 키워드이다.
- 주변의 컨텍스트를 바탕으로 타입을 추론하여 변수의 데이터 유형을 감지한다.
- 'var' 키워드를 인스턴스 변수나 전역변수 선언에는 사용 할 수 없다.
class Demo1 { // cannot use like it var x = 10; public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(x); } }- 제네릭 타입에는 사용할 수 없다
import java.util.*; class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // cannot use like it var<var> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(10); list.add(20); list.add(30); System.out.println(list); } }- 명시적인 초기화 없이는 var 키워드를 사용 할 수 없다
import java.io.*; class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // declaration without initialization // cannot use like it var variable // this is also not valid var variable = null; } }- Lambda 표현식에서 var 키워드를 사용 할 수 없다.
import java.util.*; interface myInt { int add(int a, int b); } class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { // cannot be used like it // they require explicit target type var obj = (a, b) -> (a + b); System.out.println(obj.add(2, 3)); } }- 파라미터 타입이나 리턴타입으로 var 키워드를 사용할 수 없다
class Demo5 { // method1 using var as a return type var method1() { return ("Inside Method1"); } // method2 using var for a parameter void method2(var a) { System.out.println(a); } public static void main(String[] args) { Demo obj = new Demo(); var res = obj.method1(); obj.method2(); } }References.
www.oreilly.com/library/view/java-8-pocket/9781491901083/ch04.html
Java 8 Pocket Guide
Chapter 4. Reference Types Reference types hold references to objects and provide a means to access those objects stored somewhere in memory. The memory locations are irrelevant to programmers. All … - Selection from Java 8 Pocket Guide [Book]
www.oreilly.com
www.geeksforgeeks.org/literals-in-java/
Literals in Java - GeeksforGeeks
A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
www.geeksforgeeks.org
docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/datatypes.html
Primitive Data Types (The Java™ Tutorials > Learning the Java Language > Language Basics)
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available. See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated
docs.oracle.com
Java Scope
Java Scope Java Scope In Java, variables are only accessible inside the region they are created. This is called scope. Method Scope Variables declared directly inside a method are available anywhere in the method following the line of code in which they we
www.w3schools.com
www.learningjournal.guru/article/programming-in-java/scope-and-lifetime-of-a-variable/
Scope and Lifetime of a Variable in Java - Learning Journal
One of the frequent questions, which any programmer comes across in the programming world is, “What is the scope of this variable?” In this article, our main concern is to shed light upon the scope and lifetime of a variable in Java. The scope of a var
www.learningjournal.guru
www.geeksforgeeks.org/var-keyword-in-java/
var keyword in Java - GeeksforGeeks
A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
www.geeksforgeeks.org